Explain Differences Between Hydrophytes and Hygrophytes
The hydrophyta is further subdivided into natantia not fixed to the substratum. Up to 10 cash back Differences between river types based on data collected between 2004 and 2006 by the former National Water Institute.

What Are Hydrophytes Definition Features Types Biology Reader
Hydrophytes- species living more or less permanently immersed in water.

. In contrast the amphibious plants contain well-developed xylem towards the central region. In hydrophytes the presence of endodermis and pericycle are distinct. Is that curvilinear is having bends.
The difference between hydrophytes and hygrophytes is that hydrophytes i. Species living more or less permanently immersed in water such as water lilies. Is that geohydrology is hydrogeology and hydrogeology is the geology of groundwater.
Hydrophytes mesophytes and xerophytes. The difference between kebab and burrito is that kebab is a dish of piec. Xerophytes are plants that have adapted to grow in areas with low or no precipitation at all.
The difference between aryl and arene. Hydrophytes represent a group of plants which are part of the aquatic ecosystem where most of the plants live in water or the soil saturated with water. High profile diatoms were strongly associated with hygrophytes not with hydrophytes as predicted and also with helophytes.
The floristic richness of the aquatic and hygrophytic vegetation of 27 permanent and temporary small lakes located in the León province was analyzed. Up to 10 cash back Differences were also found between hydrophytes and hygrophytes. The plants live in such a habitat where water content is in excess and.
Stomata are totally absent in submerged hydrophytes. Hydrophytes- species living more or less permanently immersed in water. Halophytes are sufficient to restore saline and contaminated lands and may become an important component of the 21st-century farming system.
The higher plants of hydrophytes have been evolved from the mesophytes. Cuticle may be present as a thin film on surface of parts exposed to atmosphere. Learn about the adaptations of three types of plants.
Explore what adaptations are and what differentiates plants that thrive in water grasslands and dry. Is that aryl is any univalent organic radical derived from an aromatic hydrocarbon by removing a hydrogen atom and arene is any monocyclic or polycyclic. Secondary growth in stems and roots does not occur in hydrophytes.
Hydrophytes only presented significant relationships with elevation and area while hygrophytes showed patterns quite similar to the total SR. These sometimes refer as macrophytes and are the common components of wetland. Submerged hydrophytes have poorly-developed xylem and tracheids.
Water lilies Hygrophytes- moisture-loving plants that generally require frequent soakings with water. In contrast FD seemed to be more resistant to environmental variables. Hydrophytes - those that are completely submersed in water - Hygrophytes - those that require frequent water soakings such as ferns and mosses - Extensive root systems or wider trunks to anchor plants - Some with pliable stems and supported by buoyancy of water instead of stems such as water lillies.
Lemna Ceratophyllum etc radicantia fixed to the substratum and adnata fixed on rocks or on other plants. Hydrophytes are plants that have adapted to grow in areas of high precipitation or inside waterbodies. They have an extensive root system which helps them reach underground water.
Halophytes are a viable commercial alternative to traditional crops and can be used as forage and animal feeds and as energy oilseed and protein crops. They are also called desert plants. Describe some typical hygrophytic adaptations of plants.
The first one is when species living more or less permanently immersed in water like water lilies while the other is moisture loving plants that generally require frequent soakings with water like ferns mosses and rushes. The evaluation of these wetlands was carried out specifying their significance at a European. Eg Podostemon Fontinalis etc.
The difference between curvilinear and projectile. Refers to plants structurally adapting to withstand protracted wet conditions. Epidermal cells are with chloroplast useful for absorption and assimilation.
Cuticle is completely absent in submerged parts of the plants. The difference between hydrophytes and hygrophytes is that hydrophytes i. The difference between geohydrology and hydrogeology.
Anatomical Features of Hydrophytes. Two types hydrophytes and hygrophytes. 158 Conclusion and future aspects.
Hygrophytes- moisture-loving plants that generally require frequent soakings with water. Is that hydrophyte is botany a plant that lives in or requires an abundance of water usually excluding seaweed while hygrophyte is biology any plant that grows wholly in water either rooted to the bottom or floating freely. Danserau classified all aquatic forms into two broad typeshelophyta paludous and hydrophyta.
The difference between swale and culvert is that swale is a low tract of. Curvilineal and projectile is an object intended to be or having been fired from a weapon. The difference between hydrophytes and hygrophytes is that.
In middle reaches grazers were strongly associated with hygrophytes and not with. Ferns mosses and rushes. As nouns the difference between hydrophyte and hygrophyte.
The difference between hydrophytes and hygrophytes is that hydrophytes i. What is the difference between Aryl and Arene. Moisture loving plants that generally require frequent soakings with water as ddo many ferns mosses and rushes.
Ferns mosses and rushes. Two groups being - hydrophytes and hygrophytes.
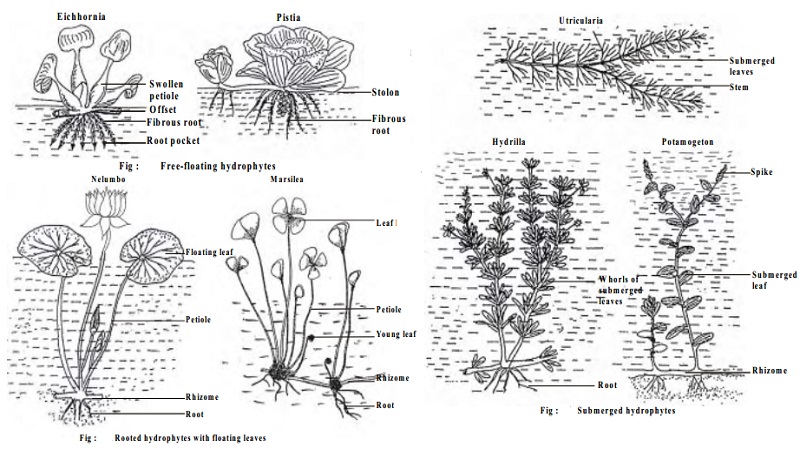
Hydrophytes And Classification Of Hydrophytes
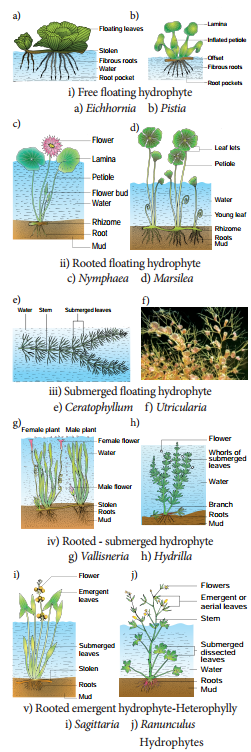
Ecological Adaptations Hydrophytes Xerophytes Mesophytes Epiphytes Halophytes Tet Success Key

Hydrophytes Everything Ponds Com
What Is The Difference Between Xerophytes Mesophytes Epiphytes And Hydrophytes Quora
No comments for "Explain Differences Between Hydrophytes and Hygrophytes"
Post a Comment